1377 start with P start with P

A law professor and former prosecutor reveals how inconsistent ideas about violence, enshrined in law, are at the root of the problems that plague our entire criminal justice system—from mass incarceration to police brutality.
We take for granted that some crimes are violent and others aren’t. But how do we decide what counts as a violent act? David Alan Sklansky argues that legal notions about violence—its definition, causes, and moral significance—are functions of political choices, not eternal truths. And these choices are central to failures of our criminal justice system.
The common distinction between violent and nonviolent acts, for example, played virtually no role in criminal law before the latter half of the twentieth century. Yet to this day, with more crimes than ever called “violent,” this distinction determines how we judge the seriousness of an offense, as well as the perpetrator’s debt and danger to society. Similarly, criminal law today treats violence as a pathology of individual character. But in other areas of law, including the procedural law that covers police conduct, the situational context of violence carries more weight. The result of these inconsistencies, and of society’s unique fear of violence since the 1960s, has been an application of law that reinforces inequities of race and class, undermining law’s legitimacy.
A Pattern of Violence shows that novel legal philosophies of violence have motivated mass incarceration, blunted efforts to hold police accountable, constrained responses to sexual assault and domestic abuse, pushed juvenile offenders into adult prisons, encouraged toleration of prison violence, and limited responses to mass shootings. Reforming legal notions of violence is therefore an essential step toward justice.

Sylvanus brings wax cloth’s unique and complex history to light: born as a nineteenth-century Dutch colonial effort to copy Javanese batik cloth for Southeast Asian markets, it was reborn as a status marker that has dominated the visual economy of West African markets. Although most wax cloth is produced in China today, it continues to be central to the expression of West African women’s identity and power. As Sylvanus shows, wax cloth expresses more than this global motion of goods, capital, aesthetics, and labor—it is a form of archive where intimate and national memories are stored, always ready to be reanimated by human touch. By uncovering this crucial aspect of West African material culture, she enriches our understanding of global trade, the mutual negotiations that drive it, and the how these create different forms of agency and subjectivity.

This uniquely comprehensive study analyzes genetic and cultural variation in a human population of extraordinary diversity. The author measures the relationship between patterns of biological and patterns of cultural variation as a way to test the contribution made by natural selection to genetic variability. If linguistic similarity and migration history serve to predict biological patterns, support is provided for the hypothesis that forces other than natural selection are responsible for the diversity observed.
The data for this study come from a group of eighteen villages located in eight neighboring language areas that are clustered in a small region of Bougainville Island, Papua New Guinea. Biological and anthropological data are analyzed with a battery of sophisticated statistical and taxonomic methods: multiple discriminant analyses, principal coordinates analyses, principal components analyses, and Gower's R2 comparison. Diverse biological properties of the Bougainville Islanders prove to be closely related to their patterns of migration. Although this result in no way refutes the role of natural selection in the evolutionary process, it highlights the extent to which genetic diversity can be molded, at least in human populations, by nonselective events.

He considers how contemporary police institutions have developed. Police forces worldwide tend to be public rather than private, to concentrate on crime fighting rather than services, and to be professionally trained and recruited. There is, however, great variation in the structure of police forces, which are generally either centralized or, as in the United States, decentralized.
The behavior of the police toward their constituents also varies by nation. As urbanization and industrialization increase, the public finds itself in greater contact with police and may begin to rely on them more for protection. There are also marked differences cross-nationally in the way police relate to political and community life.


Patterns of Time will be valued for its several distinctive achievements. Foremost among these is a demonstration of the importance of "temporality" as a topic in its own right. Because measurements of time are a commonplace of social life, sociologists have tended to ignore the significance of temporality as a feature of social organizations. Zerubavel's work is a corrective to this neglect. In addition, the author's imaginative integration of ethnographic description and theoretical analysis bridges the gap between contrasting methods that has characterized much recent sociological and anthropological work. Finally, because of the author's selection of the hospital setting, sociologists of medicine and the professions will find his study useful for its rich and well-observed ethnography, as well as its novel analytical approach.

General George S. Patton’s legendary image was carefully crafted during World War II and continues to shape our understanding of American history and culture today. Historian Nathan C. Jones explores the creation of the Patton legend and its enduring legacy in Patton’s Shadow.

Actor and singer Paul Robeson's performances in Othello, Show Boat, and The Emperor Jones made him famous, but his midcentury appearances in support of causes ranging from labor and civil rights to antilynching and American warmongering made him notorious. When Robeson announced at the 1949 Paris Peace Conference that it was "unthinkable" for blacks to go to war against the Soviet Union, the mainstream American press declared him insane.
Notions of Communism, blackness, and insanity were interchangeably deployed during the Cold War to discount activism such as Robeson's, just a part of an array of social and cultural practices that author Tony Perucci calls the Cold War performance complex. Focusing on two key Robeson performances---the concerts in Peekskill, New York, in 1949 and his appearance before the House Committee on Un-American Activities in 1956---Perucci demonstrates how these performances and the government's response to them are central to understanding the history of Cold War culture in the United States. His book provides a transformative new perspective on how the struggle over the politics of performance in the 1950s was also a domestic struggle over freedom and equality. The book closely examines both of these performance events as well as artifacts from Cold War culture---including congressional documents, FBI files, foreign policy papers, the popular literature on mental illness, and government propaganda films---to study the operation of power and activism in American Cold War culture.

“A fine, taut analysis of the great African American athlete, singer, actor, and political activist.”
—Choice, Highly Recommended
Paul Robeson should be remembered today as the forerunner of Malcolm X, Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. and Muhammad Ali. He sacrificed his fame and fortune a performer and athlete in order to fight for the rights of African Americans during the time of Jim Crow and U.S. Apartheid.
A world-famous singer and actor, a trained lawyer, an early star of American professional football and a polyglot who spoke over a dozen languages: these could be the crowning achievements of a life well-lived. Yet for Paul Robeson the higher calling of social justice led him to abandon both the NFL and Hollywood and become one of the most important political activists of his generation, a crusader for freedom and equality who battled both Jim Crow and US Senator Joseph McCarthy during the communist witch hunt of the 1950s.
In Paul Robeson: The Artist as Revolutionary, Gerald Horne discovers within Robeson's remarkable and revolutionary life the story of the twentieth century's great political struggles: against racism, against colonialism, against poverty—and for international socialism. Chapters include:
*”The Best Known American in the World"
*Rising Revolutionary
*From Moscow to Madrid
*"Black Stalin"?
*Robeson: Primary Victim of the "Blacklist"
*Triumph—and Tragedy
*Death of a Revolutionary
In the Introduction, Horne writes: “Paul Robeson—activist, artist, athlete—experienced a dramatic rise and fall, perhaps unparalleled in U.S. history. From mingling with the elite of London society and Hollywood in the 1930s, by the time he died in 1976, he was a virtual recluse in a plain abode in a working-class neighborhood of Philadelphia. What helps to explicate this tragic art of his life is a fateful decision he made when fascism was rising: he threw in his lot with those battling for socialism and decide to sacrifice his thriving artistic career on behalf of the struggle against Jim Crow—or U.S. apartheid.”
This critical and searching biography provides an opportunity for readers to comprehend the triumphs and tragedies of the revolutionary progressive movement of which Paul Robeson was not just a part, but perhaps its most resonant symbol.


Two young women, dormitory mates, embark on their education at a big state university. Five years later, one is earning a good salary at a prestigious accounting firm. With no loans to repay, she lives in a fashionable apartment with her fiancé. The other woman, saddled with burdensome debt and a low GPA, is still struggling to finish her degree in tourism. In an era of skyrocketing tuition and mounting concern over whether college is "worth it," Paying for the Party is an indispensable contribution to the dialogue assessing the state of American higher education. A powerful exposé of unmet obligations and misplaced priorities, it explains in vivid detail why so many leave college with so little to show for it.
Drawing on findings from a five-year interview study, Elizabeth Armstrong and Laura Hamilton bring us to the campus of "MU," a flagship Midwestern public university, where we follow a group of women drawn into a culture of status seeking and sororities. Mapping different pathways available to MU students, the authors demonstrate that the most well-resourced and seductive route is a "party pathway" anchored in the Greek system and facilitated by the administration. This pathway exerts influence over the academic and social experiences of all students, and while it benefits the affluent and well-connected, Armstrong and Hamilton make clear how it seriously disadvantages the majority.
Eye-opening and provocative, Paying for the Party reveals how outcomes can differ so dramatically for those whom universities enroll.

On November 16, 1989, on the campus of El Salvador's University of Central America, six Jesuits and two women were murdered by members of the Salvadoran army, an army funded and trained by the United States. One of the murdered Jesuits was Ignacio Ellacuría, the university's Rector and a key, although controversial, figure in Salvadoran public life. From an opening account of this terrible crime, Paying the Price asks, Why were they killed and what have their deaths meant? Answers come through Teresa Whitfield's detailed examination of Ellacuría's life and work. His story is told in juxtaposition with the crucial role played by the unraveling investigation of the Jesuits' murders within El Salvador's peace process.
A complex and nuanced book, Paying the Price offers a history of the Church in El Salvador in recent decades, an analysis of Ellacuría's philosophy and theology, an introduction to liberation theology, and an account of the critical importance of the University of Central America. In the end, Whitfield's comprehensive picture of conditions in El Salvador suggest that the Jesuits' murders were almost inevitable. A crime that proved a turning point in El Salvador's civil war, the murders expressed the deep tragedy of the Salvadoran people beyond suffering the heartless cruelty, violence, and deceitfulness of a corrupt military and their patrons in the U.S. government.
Whitfield draws on her extensive research of Jesuit archives and private papers, Ellacuría's diaries, documents declassified by the U.S. government, and 200 interviews conducted with sources ranging from Jesuits to Salvadoran military officers, U.S. officials and congressmen to human rights campaigners.
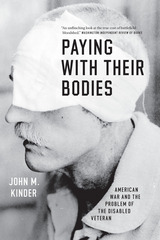
America has grappled with the questions posed by injured veterans since its founding, and with particular force since the early twentieth century: What are the nation’s obligations to those who fight in its name? And when does war’s legacy of disability outweigh the nation’s interests at home and abroad? In Paying with Their Bodies, John M. Kinder traces the complicated, intertwined histories of war and disability in modern America. Focusing in particular on the decades surrounding World War I, he argues that disabled veterans have long been at the center of two competing visions of American war: one that highlights the relative safety of US military intervention overseas; the other indelibly associating American war with injury, mutilation, and suffering. Kinder brings disabled veterans to the center of the American war story and shows that when we do so, the history of American war over the last century begins to look very different. War can no longer be seen as a discrete experience, easily left behind; rather, its human legacies are felt for decades.
The first book to examine the history of American warfare through the lens of its troubled legacy of injury and disability, Paying with Their Bodies will force us to think anew about war and its painful costs.

One contributor, a longtime president of the American Council of Learned Societies, calls for "intellectual philanthropy" and suggests that academics should transcend their ideological differences and form cooperative partnerships in the public service. A pair of essays, by key figures of the 1989 Velvet Revolution in Eastern Europe, analyze the ways that self-confidence and self-regard undercut efforts toward the resolution of complex social problems. The qualities of ideological self-subversion and even weakness, Common Knowledge maintains, are essential if the intellectual community is to become an agent for peace in a time of war.
Contributors. Wayne Andersen, Sissela Bok, Yves Bonnefoy, Caroline Walker Bynum, Clare Cavanagh, Charles-Albert Cingria, Caryl Emerson, Clifford Geertz, Stanley N. Katz, Aileen Kelly, Adam Michnik, Péter Nádas, Eugene Ostashevsky, Jeffrey M. Perl, Marjorie Perloff, Nina Pelikan Straus, Rei Terada, Gianni Vattimo, William Vesterman, Aleksandr Vvedensky, Adam Zagajewski.

Growing numbers of people are displaced by war and violent conflict. In Ukraine, Afghanistan, Ethiopia, Myanmar, Syria, and elsewhere violence pushes civilian populations from their homes and sometimes from their countries, making them refugees. In previous decades, millions of refugees and displaced people returned to their place of origin after conflict or were resettled in countries in the Global North. Now displacements last longer, the number of people returning home is lower, and opportunities for resettlement are shrinking. More and more people spend decades in refugee camps or displaced within their own countries, raising their children away from their home communities and cultures. In this context, international policies encourage return to place of origin.
Using case studies and first-person accounts from interviews and fieldwork in post-conflict settings such as Uganda, Liberia, and Kosovo, Sandra F. Joireman highlights the divergence between these policies and the preferences of conflict-displaced people. Rather than looking from the top down, at the rights that people have in international and domestic law, the perspective of this text is from the ground up—examining individual and household choices after conflict. Some refugees want to go home, some do not want to return, some want to return to their countries of origin but live in a different place, and others are repatriated against their will when they have no other options. Peace, Preference, and Property suggests alternative policies that would provide greater choice for displaced people in terms of property restitution and solutions to displacement.

Does biology condemn the human species to violence and war? Previous studies of animal behavior incline us to answer yes, but the message of this book is considerably more optimistic. Without denying our heritage of aggressive behavior, Frans de Waal describes powerful checks and balances in the makeup of our closest animal relatives, and in so doing he shows that to humans making peace is as natural as making war.
In this meticulously researched and absorbing account, we learn in detail how different types of simians cope with aggression, and how they make peace after fights. Chimpanzees, for instance, reconcile with a hug and a kiss, whereas rhesus monkeys groom the fur of former adversaries. By objectively examining the dynamics of primate social interactions, de Waal makes a convincing case that confrontation should not be viewed as a barrier to sociality but rather as an unavoidable element upon which social relationships can be built and strengthened through reconciliation.
The author examines five different species—chimpanzees, rhesus monkeys, stump-tailed monkeys, bonobos, and humans—and relates anecdotes, culled from exhaustive observations, that convey the intricacies and refinements of simian behavior. Each species utilizes its own unique peacemaking strategies. The bonobo, for example, is little known to science, and even less to the general public, but this rare ape maintains peace by means of sexual behavior divorced from reproductive functions; sex occurs in all possible combinations and positions whenever social tensions need to be resolved. “Make love, not war” could be the bonobo slogan.
De Waal’s demonstration of reconciliation in both monkeys and apes strongly supports his thesis that forgiveness and peacemaking are widespread among nonhuman primates—an aspect of primate societies that should stimulate much needed work on human conflict resolution.

In this first-ever ethnography of American gay suburbanites, Wayne H. Brekhus demonstrates that who one is depends at least in part on where and when one is. For many urban gay men, being homosexual is key to their identity because they live, work, and socialize in almost exclusively gay circles. Brekhus calls such men "lifestylers" or peacocks. Chameleons or "commuters," on the other hand, live and work in conventional suburban settings, but lead intense gay social and sexual lives outside the suburbs. Centaurs, meanwhile, or "integrators," mix typical suburban jobs and homes with low-key gay social and sexual activities. In other words, lifestylers see homosexuality as something you are, commuters as something you do, and integrators as part of yourself.
Ultimately, Brekhus shows that lifestyling, commuting, and integrating embody competing identity strategies that occur not only among gay men but across a broad range of social categories. What results, then, is an innovative work that will interest sociologists, psychologists, anthropologists, and students of gay culture.

In Peak Oil, Matthew Schneider-Mayerson takes readers deep inside the world of “peakists,” showing how their hopes and fears about the postcarbon future led them to prepare for the social breakdown they foresee—all of which are fervently discussed and debated via websites, online forums, videos, and novels. By exploring the worldview of peakists, and the unexpected way that the fear of peak oil and climate change transformed many members of this left-leaning group into survivalists, Schneider-Mayerson builds a larger analysis of the rise of libertarianism, the role of oil in modern life, the political impact of digital technologies, the racial and gender dynamics of post-apocalyptic fantasies, and the social organization of environmental denial.


This book brings together the research into regional development and social change carried out in highland Peru by a team of British and Latin American social anthropologists and sociologists. The area studied—the Mantaro Valley of central Peru—is one of the most densely populated and economically differentiated of highland zones; it is also notable for its community-based forms of cooperation and its high level of peasant political activity.
The book presents a series of case studies that examine cooperative forms of organization in relation to developments in the regional economy and to changes in national policy. The analysis attempts to avoid interpreting local processes merely as responses to externally initiated change. It stresses instead the need to consider the interplay of local and national forces, because local groups and processes themselves affect the pattern of regional and national development. The case studies cover a range of political and economic topics, from peasant movements to the achievements and shortcomings of government-sponsored agricultural and manufacturing cooperatives. The concluding chapter, by the editors, explores the theoretical implications of these studies.

Professor Dorson traces the historical development of folklore as a field of learning, beginning with sixteenth-century antiquarians whose studies encompassed the preservation of local customs and reaching its climax with the "Great Team" of Andrew Lang and his co-workers from the 1870's to the First World War.

Scholars who study peasant society now realize that peasants are not passive, but quite capable of acting in their own interests. But, do coherent political ideas emerge within peasant society or do peasants act in a world where elites define political issues? Peasant Intellectuals is based on ethnographic research begun in 1966 and includes interviews with hundreds of people from all levels of Tanzanian society. Steven Feierman provides the history of the struggles to define the most basic issues of public political discourse in the Shambaa-speaking region of Tanzania. Feierman also shows that peasant society contains a rich body of alternative sources of political language from which future debates will be shaped.


Focusing on peasant struggles for market control over coffee exports in Bugisu from colonial times through the reign and overthrow of Idi Amin, Bunker shows that these freeholding peasants acted collectively and used the state's dependence on coffee export revenues to effectively influence and veto government programs inimical to their interests.
Bunker's work vividly portrays the small victories and great trials of ordinary people struggling to control their own economic destiny while resisting the power of the world economy.


Based on extended interviews at the Culiprán fundo in Chile with peasants who recount in their own terms their political evolution, this is an in-depth study of peasants in social and political action. It deals with two basic themes: first, the authoritarian structure within a traditional latifundio and its eventual replacement by a peasant-based elected committee, and second, the events shaping the emergence of political consciousness among the peasantry. Petras and Zemelman Merino trace the careers of local peasant leaders, followers, and opponents of the violent illegal land seizure in 1965 and the events that triggered the particular action.
The findings of this study challenge the oft-accepted assumption that peasants represent a passive, traditional, downtrodden group capable only of following urban-based elites. The peasant militants, while differing considerably in their ability to grasp complex political and social problems, show a great deal of political skill, calculate rationally on the possibility of success, and select and manipulate political allies on the basis of their own primary needs. The politicized peasantry lend their allegiance to those forces with whom they anticipate they have the most to gain—and under circumstances that minimize social costs. The authors identify the highly repressive political culture within the latifundio—reinforced by the national political system—as the key factor inhibiting overt expressions of political demands.
The emergence of revolutionary political consciousness is found to be the result of cumulative experiences and the breakdown of traditional institutions of control. The violent illegal seizure of the farm is perceived by the peasantry as a legitimate act based on self-interest as well as general principles of justice—in other words, the seizure is perceived as a “natural act,” suggesting that perhaps two sets of moralities functioned within the traditional system.
The book is divided into two parts: the first part contains a detailed analysis of peasant behavior; the second contains transcriptions of peasant interviews. Combined, they give the texture and flavor of insurgent peasant politics.

Grounded in the theoretical perspectives of subaltern studies and drawing on an extremely complete archive of landed estates that includes detailed regular reports by plantation managers on all aspects of farming life, Peasants on Plantations reveals the intricate ways peasants, managers, and owners manipulated each other to benefit their own interests. As Peloso demonstrates, rather than a simple case of domination of the peasants by the owners, both parties realized that negotiation was the key to successful growth, often with the result that peasants cooperated with plantation growth strategies in order to participate in a market economy. Long-term contracts gave tenants and sharecroppers many opportunities to make farming choices, to assert claims on the land, compete among themselves, and participate in plantation expansion. At the same time, owners strove to keep the peasants in debt and well aware of who maintained ultimate control.
Peasants on Plantations offers a largely untold view of the monumental struggle between planters and peasants that was fundamental in shaping the agrarian history of Peru. It will interest those engaged in Latin American studies, anthropology, and peasant and agrarian studies.

Throughout Latin America and the rest of the Third World, profound social problems are growing in response to burgeoning populations and unstable economic and political systems. In Peru, terrorist acts by the Shining Path guerilla movement are the most visible manifestation of social discontent, but rapid economic and religious changes have touched the lives of almost everyone, radically altering traditional lifeways. In this twenty-year study of the community of Quinua in the Department of Ayacucho, William Mitchell looks at changes provoked by population growth within a severely limited ecological and economic setting, including increasing conversion to a cash economy and out-migration, the decline of the Catholic fiesta system and the rise of Protestantism, and growing poverty and revolution.
When Mitchell first began his field studies in Quinua in 1966, farming was still the Quinueños' principal means of livelihood. But while the population was increasing rapidly, the amount of arable land in the community remained the same, creating increased food shortfalls. At the same time, government controls on food prices and subsidies of cheap food imports drove down the value of rural farm production. These ecological and economic factors forced many people to enter the nonfarm economy to feed themselves.
Using a materialist approach, Mitchell charts the new economic strategies that Quinueños use to confront the harsh pressures of their lives, including ceramic production, wage labor, petty commerce, and migration to cash work on the coat and in the eastern tropical forests. In addition, he shows how the growing conversion from Catholicism to Protestantism is also an economic strategy, since Protestant ideology offers acceptable reasons for redirecting the money that used to be spent on elaborate religious festivals to household needs and education.
The twenty-year span of this study makes it especially valuable for students of social change. Mitchell's unique, interdisciplinary approach, considering ecological, economic, and population factors simultaneously, offers a model that can be widely applied in many Third World areas. Additionally, the inclusion of an entire chapter of family histories reveals how economic and ecological forces are played out at the individual level.

A trenchant case for a novel philosophical position: that our political thinking is driven less by commitments to freedom or fairness than by an aversion to hierarchy.
Niko Kolodny argues that, to a far greater extent than we recognize, our political thinking is driven by a concern to avoid relations of inferiority. In order to make sense of the most familiar ideas in our political thought and discourse—the justification of the state, democracy, and rule of law, as well as objections to paternalism and corruption—we cannot merely appeal to freedom, as libertarians do, or to distributive fairness, as liberals do. We must instead appeal directly to claims against inferiority—to the conviction that no one should stand above or below.
The problem of justifying the state, for example, is often billed as the problem of reconciling the state with the freedom of the individual. Yet, Kolodny argues, once we press hard enough on worries about the state’s encroachment on the individual, we end up in opposition not to unfreedom but to social hierarchy. To make his case, Kolodny takes inspiration from two recent trends in philosophical thought: on the one hand, the revival of the republican and Kantian traditions, with their focus on domination and dependence; on the other, relational egalitarianism, with its focus on the effects of the distribution of income and wealth on our social relations.
The Pecking Order offers a detailed account of relations of inferiority in terms of objectionable asymmetries of power, authority, and regard. Breaking new ground, Kolodny looks ahead to specific kinds of democratic institutions that could safeguard against such relations.

Alfred V. Kidder’s excavations at Pecos Pueblo in New Mexico between 1914 and 1929 set a new standard for archaeological fieldwork and interpretation. Among his other innovations, Kidder recognized that skeletal remains were a valuable source of information, and today the Pecos sample is used in comparative studies of fossil hominins and recent populations alike.
In the 1990s, while documenting this historic collection in accordance with the Native American Graves Protection and Repatriation Act before the remains were returned to the Pueblo of Jemez and reinterred at Pecos Pueblo, Michèle E. Morgan and colleagues undertook a painstaking review of the field data to create a vastly improved database. The Peabody Museum, where the remains had been housed since the 1920s, also invited a team of experts to collaboratively study some of the materials.
In Pecos Pueblo Revisited, these scholars review some of the most significant findings from Pecos Pueblo in the context of current Southwestern archaeological and osteological perspectives and provide new interpretations of the behavior and biology of the inhabitants of the pueblo. The volume also presents improved data sets in extensive appendices that make the primary data available for future analysis. The volume answers many existing questions about the population of Pecos and other Rio Grande sites and will stimulate future analysis of this important collection.

A Peculiar Imbalance is the little-known history of the black experience in Minnesota in the mid-1800s, a time of dramatic change in the region. William D. Green explains how, as white progressive politicians pushed for statehood, black men who had been integrated members of the community, owning businesses and maintaining good relationships with their neighbors, found themselves denied the right to vote or to run for office in those same communities.
As Minnesota was transformed from a wilderness territory to a state, the concepts of race and ethnicity and the distinctions among them made by Anglo-Americans grew more rigid and arbitrary. A black man might enjoy economic success and a middle-class lifestyle but was not considered a citizen under the law. In contrast, an Irish Catholic man was able to vote—as could a mixed-blood Indian—but might find himself struggling to build a business because of the ethnic and religious prejudices of the Anglo-American community. A Peculiar Imbalance examines these disparities, reflecting on the political, social, and legal experiences of black men from 1837 to 1869, the year of black suffrage.

The U.S. death penalty is a peculiar institution, and a uniquely American one. Despite its comprehensive abolition elsewhere in the Western world, capital punishment continues in dozens of American states– a fact that is frequently discussed but rarely understood. The same puzzlement surrounds the peculiar form that American capital punishment now takes, with its uneven application, its seemingly endless delays, and the uncertainty of its ever being carried out in individual cases, none of which seem conducive to effective crime control or criminal justice. In a brilliantly provocative study, David Garland explains this tenacity and shows how death penalty practice has come to bear the distinctive hallmarks of America’s political institutions and cultural conflicts.
America’s radical federalism and local democracy, as well as its legacy of violence and racism, account for our divergence from the rest of the West. Whereas the elites of other nations were able to impose nationwide abolition from above despite public objections, American elites are unable– and unwilling– to end a punishment that has the support of local majorities and a storied place in popular culture.
In the course of hundreds of decisions, federal courts sought to rationalize and civilize an institution that too often resembled a lynching, producing layers of legal process but also delays and reversals. Yet the Supreme Court insists that the issue is to be decided by local political actors and public opinion. So the death penalty continues to respond to popular will, enhancing the power of criminal justice professionals, providing drama for the media, and bringing pleasure to a public audience who consumes its chilling tales.
Garland brings a new clarity to our understanding of this peculiar institution– and a new challenge to supporters and opponents alike.

A Peculiar Paradise: A History of Blacks in Oregon 1788–1940 remains the most comprehensive chronology of Black life in Oregon more than forty years after its original publication in 1980. The book has long been a resource for those seeking information on the legal and social barriers faced by people of African descent in Oregon. Elizabeth McLagan’s work reveals how in spite of those barriers, Black individuals and families made Oregon their home, and helped create the state’s modern Black communities. Long out of print, the book is available again through this co-publication with Oregon Black Pioneers, Oregon’s statewide African American historical society. The revised second edition includes additional details for students and scholars, an expanded reading list, a new selection of historic images, and a new foreword by Gwen Carr and an afterword by Elizabeth McLagan.

Sensationalized accounts of white rural communities’ aberrant sexualities, racial intermingling, gender transgressions, and anomalous bodies and minds, which proliferated from the turn of the century, created a national view of the perversity of white rural poverty for the American public. Cartwright contends that these accounts, extracted and estranged from their own ambivalent forum of community gossip, must be read in kind: through a racialized, materialist queercrip optic of the deeply familiar and mundane. Taking in popular science, documentary photography, news media, documentaries, and horror films, Peculiar Places orients itself at the intersections of disability studies, queer studies, and gender studies to illuminate a racialized landscape both profoundly ordinary and familiar.


In these meditations, Alexander deftly unites large, often contradictory, historical processes across time and space. She focuses on the criminalization of queer communities in both the United States and the Caribbean in ways that prompt us to rethink how modernity invents its own traditions; she juxtaposes the political organizing and consciousness of women workers in global factories in Mexico, the Caribbean, and Canada with the pressing need for those in the academic factory to teach for social justice; she reflects on the limits and failures of liberal pluralism; and she presents original and compelling arguments that show how and why transgenerational memory is an indispensable spiritual practice within differently constituted women-of-color communities as it operates as a powerful antidote to oppression. In this multifaceted, visionary book, Alexander maps the terrain of alternative histories and offers new forms of knowledge with which to mold alternative futures.

The pressures Asian Americans feel to be socially and economically exceptional include an unspoken mandate to always be healthy. Nowhere is this more evident than in the expectation for Asian Americans to enter the field of medicine, principally as providers of care rather than those who require care. Pedagogies of Woundedness explores what happens when those considered model minorities critically engage with illness and medicine whether as patients or physicians.
James Kyung-Jin Lee considers how popular culture often positions Asian Americans as medical authorities and what that racial characterization means. Addressing the recent trend of writing about sickness, disability, and death, Lee shows how this investment in Asian American health via the model minority is itself a response to older racial forms that characterize Asian American bodies as diseased. Moreover, he pays attention to what happens when academics get sick and how illness becomes both methodology and an archive for scholars.
Pedagogies of Woundedness also explores the limits of biomedical “care,” the rise of physician chaplaincy, and the impact of COVID. Throughout his book and these case studies, Lee shows the social, ethical, and political consequences of these common (mis)conceptions that often define Asian Americans in regard to health and illness.

Pedagogy of Democracy re-interprets the U.S. occupation of Japan from 1945 to 1952 as a problematic instance of Cold War feminist mobilization rather than a successful democratization of Japanese women as previously argued. By combining three fields of research—occupation, Cold War, and postcolonial feminist studies—and examining occupation records and other archival sources, Koikari argues that postwar gender reform was one of the Cold War containment strategies that undermined rather than promoted women’s political and economic rights.

The essays in this collection explore the unity between cycling for health, work, competition, transport, and joy, and the issues of animal suffering, environmentalism, and speciesism inherent in veganism—all through lenses of class, race, gender, and disability. Pedaling Resistance illuminates themes of everyday resistance and boundary crossing to uncover the greater social and political issues that underlie the decisions to give up animal products and choose cycling over driving.

Pedro Pino, or Lai-iu-ah-tsai-lu (his Zuni name) was for many years the most important Zuni political leader. He served during a period of tremendous change and challenges for his people. Born in 1788, captured by Navajos in his teens, he was sold into a New Mexican household, where he obtained his Spanish name. When he returned to Zuni, he spoke three languages and brought with him a wealth of knowledge regarding the world outside the pueblo. For decades he ably conducted Zuni foreign relations, defending the pueblo's sovereignty and lands, establishing trade relationships, interacting with foreigners-from prominent military and scientific expeditions to common emigrants-and documenting all in a remarkable archive. Steeped in Zuni traditions, he was known among other things for his diplomatic savvy, as a great warrior, for his oratory, and for his honesty and hospitality.
More than a biography, Richard Hart's work provides a history of Zuni during an especially significant period. Also the author of Zuni and the Courts: A Struggle for Sovereign
Land Rights and the co-author of A Zuni Atlas, Hart originally wrote the manuscript in 1979 after a decade of historical work for Zuni Pueblo. He then set it aside but continued to pursue research about and for Zuni. Its publication, at last, inscribes an important contribution to Pueblo history and biography and a testimonial to a remarkable Native American leader. In an afterword written for this publication, Hart discusses his original intentions in writing about Pedro Pino and Zuni and situates the biography in relation to current scholarship.

The Adlers explore some of the patterns that develop in this social space, noting both the differences in boys' and girls' gendered cultures and the overlap in many social dynamics, afterschool activities, role behaviour, romantic inclinations and social stratification. For example, children's participation in adult-organized afterschool activities - a now-prominent feature of many American children's social experience - has profound implications for their socialization and development, moving them away from the negotiated, spontaneous character of play into the formal systems of adult norms and values at ever-younger ages. When they retreat from adults, however, they still display distinctive peer group dynamics, forging strong ingroup/outgroup differentiation, loyalty and identification. Peer culture thus contains informal social mechanisms through which children create their social order, determine their place and identity, and develop positive and negative feelings about themselves. Studying children's peer culture is thus valuable as it reveals not only how this subculture parallels the adult world but also how it differs from it.

A missing chapter in African American theatrical history, Bauman's saga presents how Motts used his entrepreneurial acumen to create a successful black-owned enterprise. Concentrating on institutional history, Bauman explores the Pekin's philosophy of hiring only African American staff, its embrace of multi-racial upper class audiences, and its ready assumption of roles as diverse as community center, social club, and fundraising instrument.
The Pekin's prestige and profitability faltered after Motts' death in 1911 as his heirs lacked his savvy, and African American elites turned away from pure entertainment in favor of spiritual uplift. But, as Bauman shows, the theater had already opened the door to a new dynamic of both intra- and inter-racial theater-going and showed the ways a success, like the Pekin, had a positive economic and social impact on the surrounding community.

With a population of about two thousand, Pembroke Township, one of the largest rural, black communities north of the Mason-Dixon Line, sits in an isolated corner of Kankakee County, Illinois, sixty-five miles south of Chicago. It is also one of the poorest places in the nation. Many black farmers from the South came to this area during the Great Migration; finding Chicago to be overcrowded and inhospitable, they were able to buy land in the township at low prices. The poor soil made it nearly impossible to establish profitable farms, however, and economic prosperity has eluded the region ever since. Pembroke: A Rural, Black Community on the Illinois Dunes chronicles the history of this inimitable township and shows the author’s personal transformation through his experiences with Pembroke and its people. A native of nearby Kankakee, author Dave Baron first traveled to Pembroke on a church service trip at age fifteen and saw real poverty firsthand, but he also discovered a community possessing grace and purpose.
Baron begins each chapter with a personal narrative from his initial trip to Pembroke. He covers the early history of the area, explaining how the unique black oak savanna ecosystem was created and describing early residents, including Potawatomi tribes and white fur traders. He introduces readers to Pap and Mary Tetter, Pembroke’s first black residents, who—according to local lore—assisted fugitives on the Underground Railroad; details the town’s wild years, when taverns offered liquor, drugs, and prostitution; discusses the many churches of Pembroke and the nearby high school where, in spite of sometimes strained relations, Pembroke’s black students have learned alongside white students of a neighboring community since well before Brown v. Board of Education; outlines efforts by conservation groups to preserve Pembroke’s rare black oak savannas; and analyzes obstacles to and failed attempts at economic development in Pembroke, as well as recent efforts, including organic farms and a sustainable living movement, which may yet bring some prosperity.
Based on research, interviews with residents, and the author’s own experiences during many return trips to Pembroke, this book—part social, cultural, legal, environmental, and political history and part memoir—profiles a number of the colorful, longtime residents and considers what has enabled Pembroke to survive despite a lack of economic opportunities. Although Pembroke has a reputation for violence and vice, Baron reveals a township with a rich and varied history and a vibrant culture.


At Milwaukee’s Luther Manor, a team of artists from the University of Wisconsin’s theatre department and Sojourn Theatre Company, university students, staff, residents, and volunteers traded their bingo cards for copies of The Odyssey. They embarked on a two-year project to examine this ancient story from the perspective of the hero who never left home: Penelope, wife of Odysseus. Together, the team staged a play that engaged everyone and transcended the limits not just of old age and disability but also youth, institutional regulations, and disciplinary boundaries.
Inviting readers to see through the eyes of residents, students, artists, staff, family members, and experts in the fields of education, long-term care, and civically engaged arts practice, this book underscores the essential role of the arts and humanities in living richly. Waiting, as Penelope waited, need not be a time of loss and neglect. The Penelope Project boldly dreams of how to make late life a time of growth and learning. If you dream of improving people’s lives through creative endeavors, this book provides practical advice.


MacDougall demonstrates that Penobscot legend, linguistics, dance, and oral tradition became foundations of resistance against assimilation into the dominant culture. She thoughtfully and accessibly reconstructs from published, archival, and oral sources the tribe's metaphorical and triumphant Dance of Resistance—founded on spiritual power, reverence for homeland, and commitment to self-determination—from colonial times to the present. A decade of political activism culminated in the precedent-setting 1980 Maine Indian Land Claims settlement. Today the Penobscots run small industries, manage their natural resources, and provide health services, K through 8 education, and social services to the poor and elderly of their community.


Pentecostalism in Urban Oaxaca is a timely feminist ethnography set in a Pentecostal church community in Oaxaca de Juarez. Based on extensive fieldwork, Ramirez skillfully melds medical anthropology with cultural analysis to reveal the Pentecostal movement’s dynamics in the contexts of faith healing, marital relations, and economic prosperity.
Ramirez takes stock of the problematic ways that Pentecostalism has played out for Mexican women today but also reminds readers of some of its successes. Within the context of Mexican patriarchy, some women parishioners in abusive relationships see the church as a way to improve their lot. Pentecostalism seeks to rupture with Mexico’s colonial heritage, and Ramirez provides novel ways for the reader to consider how Pentecostalism can provide healing for even the “endlessness of addiction.” One case study portrays a former abusive alcoholic womanizer who underwent a spiritual transformation as a result of his conversion. Through this example and more, Ramirez examines the complex relationship between gender, modernity, and Indigeneity in the context of marriage. The book also addresses the #MeToo movement as encountered in the Pentecostal church.
Finally, Ramirez investigates how Pentecostalism addresses the “curses” of illness and poverty, highlighting the paradoxical relationship between faith healing and curanderismo. The gospel of economic prosperity holds promise for a better life, breaking free from the “disease” of poverty. To this end, Ramirez profiles some parishioners’ involvement with Omnilife, a multilevel marketing company selling vitamins and natural health products that propounds ideals similar to those of Pentecostal Christianity.



Using the rich and vital Australian Aboriginal understanding of country as a model, People and Places of Nature and Culture affirms the importance of a sustainable relationship between nature and culture. While current thought includes the mistaken notion—perpetuated by natural history, ecology, and political economy—that humans have a mastery over the Earth, this book demonstrates the problems inherent in this view. In the current age of climate change, this is an important appraisal of the relationship between nature and culture, and a projection of what needs to change if we want to achieve environmental stability.

The most comprehensive overview in more than half a century about the interconnectedness of prehistoric Native Americans and their botanical world, this book and its forthcoming companion volume, People and Plants in Ancient Western North America, present the latest information on three major topics: the use of native plants, the history of crops and their uses, and how humans affected their environment. In this volume, expert scholars summarize the prehistoric ethnobotany of four regions: the Eastern Woodlands (W. Cowan, K. Gremillion, M. Scarry, B. Smith, and G. Wagner), Northeast (G. Crawford and D. Smith), Plains (M. Adair), and Caribbean (L. Newsom and D. Pearsall).
This volume contributes significantly to our understanding of the lives of prehistoric people as well as the forces that influenced their communities, their ingenuity, and their ecological impact. It also serves as a guide for designing environmentally sustainable lives today.

The most comprehensive overview in more than half a century on the interconnectedness of people and plants, this book and its companion volume, People and Plants in Ancient Eastern North America, present the latest information on three major topics: the uses of native plants, the history of crops and their uses, and the impact of humans on their environment. They not only contribute to our understanding of the lives of prehistoric people but also serve as guides for designing sustainable living today.

Focusing on autobiographical writings and critical essays, as well as communally authored and political documents, The People and the Word explores how the Native tradition of nonfiction has both encompassed and dissected Native experiences. Warrior begins by tracing a history of American Indian writing from the eighteenth century to the late twentieth century, then considers four particular moments: Pequot intellectual William Apess’s autobiographical writings from the 1820s and 1830s; the Osage Constitution of 1881; narratives from American Indian student experiences, including accounts of boarding school in the late 1880s; and modern Kiowa writer N. Scott Momaday’s essay “The Man Made of Words,” penned during the politically charged 1970s. Warrior’s discussion of Apess’s work looks unflinchingly at his unconventional life and death; he recognizes resistance to assimilation in the products of the student print shop at the Santee Normal Training School; and in the Osage Constitution, as well as in Momaday’s writing, Warrior sees reflections of their turbulent times as well as guidance for our own.
Taking a cue from Momaday’s essay, which gives voice to an imaginary female ancestor, Ko-Sahn, Warrior applies both critical skills and literary imagination to the texts. In doing so, The People and the Word provides a rich foundation for Native intellectuals’ critical work, deeply entwined with their unique experiences.
Robert Warrior is professor of English and Native American studies at the University of Oklahoma. He is author of Tribal Secrets: Recovering American Indian Intellectual Traditions (Minnesota, 1994) and coauthor, with Paul Chaat Smith, of Like a Hurricane: The Indian Movement from Alcatraz to Wounded Knee.

Linking archival research, ethnographic fieldwork, and oral history, Karilyn Crockett in People before Highways offers ground-level analysis of the social, political, and environmental significance of a local anti-highway protest and its lasting national implications. The story of how an unlikely multiracial coalition of urban and suburban residents, planners, and activists emerged to stop an interstate highway is one full of suspenseful twists and surprises, including for the actors themselves. And yet, the victory and its aftermath are undeniable: federally funded mass transit expansion, a linear central city park, and a highway-less urban corridor that serves as a daily reminder of the power and efficacy of citizen-led city making.


During the past thirty years, Native American dance has emerged as a visible force on concert stages throughout North America. In this first major study of contemporary Native American dance, Jacqueline Shea Murphy shows how these performances are at once diverse and connected by common influences.
Demonstrating the complex relationship between Native and modern dance choreography, Shea Murphy delves first into U.S. and Canadian federal policies toward Native performance from the late nineteenth through the early twentieth centuries, revealing the ways in which government sought to curtail authentic ceremonial dancing while actually encouraging staged spectacles, such as those in Buffalo Bill’s Wild West shows. She then engages the innovative work of Ted Shawn, Lester Horton, and Martha Graham, highlighting the influence of Native American dance on modern dance in the twentieth century. Shea Murphy moves on to discuss contemporary concert dance initiatives, including Canada’s Aboriginal Dance Program and the American Indian Dance Theatre.
Illustrating how Native dance enacts, rather than represents, cultural connections to land, ancestors, and animals, as well as spiritual and political concerns, Shea Murphy challenges stereotypes about American Indian dance and offers new ways of recognizing the agency of bodies on stage.
Jacqueline Shea Murphy is associate professor of dance studies at the University of California, Riverside, and coeditor of Bodies of the Text: Dance as Theory, Literature as Dance.

Contributors highlight how Indigenous Plains groups participated in large-scale social networks in which ideas, symbols, artifacts, and people moved across North America over the last 2,000 years. They also discuss cultural transformation, focusing on key demographic, economic, social, and ceremonial factors associated with change, including colonization and integration into the social and political economies of transatlantic societies. Cultural traditions covered include Woodland-era Kansas City Hopewell, late prehistoric Central Plains tradition, and ancestral and early historic Wichita, Pawnee and Arikara, Kanza, Plains Apache, and Puebloan migrants. As the first review of Plains archaeology in more than a decade, this book brings studies of early Indigenous
peoples of the central and southern Plains into a new era.


For fifty years anthropologist June Helm studied the culture and ethnohistory of the Dene, “The People,” the Athapaskan-speaking Indians of the Mackenzie River drainage of Canada's western subarctic. Now in this impressive collection she brings together previously published essays—with updated commentaries where necessary—unpublished field notes, archival documents, supplementary essays and notes from collaborators, and narratives by the Dene themselves as an offering to those studying North American Indians, hunter-gatherers, and subarctic ethnohistory and as a historical resource for the people of all ethnicities who live in Denendeh, Land of the Dene.
Helm begins with a broad-ranging, stimulating overview of the social organization of hunter-gatherer peoples of the world, past and present, that provides a background for all she has learned about the Dene. The chapters in part 1 focus on community and daily life among the Mackenzie Dene in the middle of the twentieth century. After two historical overview chapters, Helm moves from the early years of the twentieth century to the earliest contacts between Dene and white culture, ending with a look at the momentous changes in Dene-government relations in the 1970s. Part 3 considers traditional Dene knowledge, meaning, and enjoyments, including a chapter on the Dogrib hand game. Throughout, Helm's encyclopedic knowledge combines with her personal interactions to create a collection that is unique in its breadth and intensity.




People of the Big Voice tells the visual history of Ho-Chunk families at the turn of the twentieth century and beyond as depicted through the lens of Black River Falls, Wisconsin studio photographer, Charles Van Schaick. The family relationships between those who “sat for the photographer” are clearly visible in these images—sisters, friends, families, young couples—who appear and reappear to fill in a chronicle spanning from 1879 to 1942. Also included are candid shots of Ho-Chunk on the streets of Black River Falls, outside family dwellings, and at powwows. As author and Ho-Chunk tribal member Amy Lonetree writes, “A significant number of the images were taken just a few short years after the darkest, most devastating period for the Ho-Chunk. Invasion, diseases, warfare, forced assimilation, loss of land, and repeated forced removals from our beloved homelands left the Ho-Chunk people in a fight for their culture and their lives.”

"Gives a vivid picture, not only of tribal peoples in transition, but of the motives and methods of a dedicated, compassionate teacher in an era of forced Indian assimilation."—Books of the Southwest
"Delightful reading about an exotic life in a stupendous natural setting."—New York Times


"To read and gaze through this elegantly illustrated book is to be exposed, as if through a work of science fiction, to an astonishing and unknown cultural world."—North Dakota Quarterly

Since 1972 the Rainbow Family of Living Light, a loosely organized and anarchistic nomadic community, has been holding large gatherings in remote forests to pray for world peace and create a model of a functioning utopian society. Michael I. Niman’s People of the Rainbow, originally published in 1997, was the first comprehensive study of this countercultural group and its eclectic philosophy of environmentalism, feminism, peace activism, group sharing, libertarianism, and consensus government. It is a book yet to be superseded.
This second edition of Niman’s compelling and insightful work brings the Rainbow story up to date with a new introduction and two extensive new epilogues. While the big annual Rainbow “Gatherings” have drawn fewer numbers in recent years, Niman notes, the Rainbow ethos has in many ways migrated to the mainstream, as Rainbow notions about alternative medicine and environmental sustainability, for example, have gathered wider acceptance and influenced the national dialogue. Meanwhile, Rainbow movements in other regions, from Eastern Europe and the Middle East to Asia and Australia, are thriving.
In addition to addressing changes within the Rainbow Family and its complex relationship
to “Babylon” (what Rainbows call mainstream culture), the book’s new material explores the growing harassment Rainbows now face from U.S. law enforcement agencies—
especially those associated with the National Forest Service. As Niman contends, this particular saga of a U.S. bureaucracy at war with its own citizens is a subplot in the larger—and disturbing—story of how the relationship between Americans and their government has changed during the first decade of the twenty-first century.
In its nuanced portrait of an intriguing subculture, its successes, and its limitations, People of the Rainbow remains a significant contribution to the study of utopian communities in the United States and their ongoing legacy.
Michael I. Niman is a professor of journalism and media studies in the Communication Department at Buffalo State College in New York.
For additional resources related to this new edition, see http://buffalostate.edu/peopleoftherainbow.

The Missouria people were the first American Indians encountered by European explorers venturing up the Pekitanoui River—the waterway we know as the Missouri. This Indian nation called itself the Nyut^achi, which translates to “People of the River Mouth,” and had been a dominant force in the Louisiana Territory of the pre-colonial era. When first described by the Europeans in 1673, they numbered in the thousands. But by 1804, when William Clark referred to them as “once the most powerful nation on the Missouri River,” fewer than 400 Missouria remained. The state and Missouri River are namesakes of these historic Indians, but little of the tribe’s history is known today. Michael Dickey tells the story of these indigenous Americans in The People of the River’s Mouth.
Accessible to general readers, this book recovers the lost history of an important people. The People of the River’s Mouth sheds light on an overlooked aspect of Missouri’s past and pieces together the history of these influential Native Americans in an engaging, readable volume.

For his second edition of The People of the Sierra Julian A. Pitt-River has unmasked the village of Grazalema which had been protectively cloaked in pseudonym for the original version. In addition he has added a new preface which elaborates upon his earlier theories on norms, values, and social structure, and reconsiders them in the light of current theories of other social scientists.
Because of its unique and penetrating observations, not only Hispanic, Mediterranean, and European but also Latin American scholars regard this book as one of the foundation stones of contemporary cultural studies in several disciplines. Beyond the significance of its substance and theory, this study has considerable merit as a humane work of subtle perception and artful execution.

The Oneidas' physical, political, and emotional division persists to this day. Even for those who stayed put, their world changed more in cultural, ecological, and demographic terms than at any time before or since. Oneidas of the post-Revolutionary decades were reluctant pioneers, undertaking more of the adaptations to colonized life than any other generation. Amid such wrenching change, maintaining continuity was itself a creative challenge. The story of that extraordinary endurance lies at the heart of this book.

This collection gathers a unique group of contributors, including representatives from Congress, the United Nations, and Israel’s Ministry of Justice, as well as senior diplomats from Canada, Bulgaria, Portugal, Spain, and Turkey. Presenting their diverse perspectives, the contributors address regional and policy issues related to the mass migration of people, as well as questions concerning citizenship and national security, human trafficking in the form of prostitution, and cultural discrimination. The result is a multifaceted exploration of issues underlying many of the world’s economic, security, and social challenges. Other topics include the impact of state failure on migration, immigration in California, security measures and “preferred” immigrants in Canada after September 11, 2001, and Albanian migration into Greece.
Contributors. Alexandre Afonso, David Binder, Andrew C. Danopoulos, Constantine P. Danopoulos, Francis M. Deng, Mohamed A. El-Khawas, Omar G. Encarnación, Rochelle Gershuni, Larry L. Gerston, Ahmet Içduygu, Benjamin Kline, Bojan Korenic, Erin Kruger, Robert S. Leiken, Marlene Mulder, Elena Poptodorova, Tom Tancredo

People, Plants, and Landscapes showcases the potential of modern paleoethnobotany, an interdisciplinary field that explores the interactions between human beings and plants by examining archaeological evidence. Using different methods and theoretical approaches, the essays in this work apply botanical knowledge to studies of archaeological plant remains and apply paleoethnobotany to nonarchaeological sources of evidence. The resulting techniques often lie beyond the traditional boundaries of either archaeology or botany.
With this ground-breaking work, the technically and methodologically enhanced paleoethnobotany of the 1990s has joined forces with ecological and evolutionary theory to forge explanations of changing relationships between human and plant populations.
Contents and Contributors:
The Shaping of Modern Paleoethnobotany, Patty Jo Watson
New Perspectives on the Paleoethnobotany of the Newt Kash Shelter, Kristen J. Gremillion
A 3,000-Year-Old Cache of Crop Seeds from Marble Bluff, Arkansas, Gayle J. Fritz
Evolutionary Changes Associated with the Domestication of Cucurbita pepo: Evidence from Eastern Kentucky, C. Wesley Cowan
Anthropogenesis in Prehistoric Northeastern Japan, Gary W. Crawford
Between Farmstead and Center: The Natural and Social Landscape of Moundville, C. Margaret Scarry and Vincas P. Steponaitis
An Evolutionary Ecology Perspective on Diet Choice, Risk, and Plant Domestication, Bruce Winterhalder and Carol Goland
The Ecological Structure and Behavioral Implications of Mast Exploitation Strategies, Paul S. Gardner
Changing Strategies of Indian Field Location in the Early Historic Southeast, Gregory A. Waselkov
Interregional Patterns of Land Use and Plant Management in Native North America, Julia E. Hammett

An illuminating volume of critical essays charting the diverse territory of digital humanities scholarship
The digital humanities have traditionally been considered to be the domain of only a small number of prominent and well-funded institutions. However, through a diverse range of critical essays, this volume serves to challenge and enlarge existing notions of how digital humanities research is being undertaken while also serving as a kind of alternative guide for how it can thrive within a wide variety of institutional spaces.
Focusing on the complex infrastructure that undergirds the field of digital humanities, People, Practice, Power examines the various economic, social, and political factors that shape such academic endeavors. The multitude of perspectives comprising this collection offers both a much-needed critique of the existing structures for digital scholarship and the means to generate broader representation within the field.
This collection provides a vital contribution to the realm of digital scholarly research and pedagogy in acknowledging the role that small liberal arts colleges, community colleges, historically black colleges and universities, and other underresourced institutions play in its advancement. Gathering together a range of voices both established and emergent, People, Practice, Power offers practitioners a self-reflexive examination of the current conditions under which the digital humanities are evolving, while helping to open up new sustainable pathways for its future.
Contributors: Matthew Applegate, Molloy College; Taylor Arnold, U of Richmond; Eduard Arriaga, U of Indianapolis; Lydia Bello, Seattle U; Kathi Inman Berens, Portland State U; Christina Boyles, Michigan State U; Laura R. Braunstein, Dartmouth College; Abby R. Broughton; Maria Sachiko Cecire, Bard College; Brennan Collins, Georgia State U; Kelsey Corlett-Rivera, U of Maryland; Brittany de Gail, U of Maryland; Madelynn Dickerson, UC Irvine Libraries; Nathan H. Dize, Vanderbilt U; Quinn Dombrowski, Stanford U; Ashley Sanders Garcia, UCLA; Laura Gerlitz; Erin Rose Glass; Kaitlyn Grant; Margaret Hogarth, Claremont Colleges; Maryse Ndilu Kiese, U of Alberta; Pamella R. Lach, San Diego State U; James Malazita, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute; Susan Merriam, Bard College; Chelsea Miya, U of Alberta; Jamila Moore Pewu, California State U, Fullerton; Urszula Pawlicka-Deger, Aalto U, Finland; Jessica Pressman, San Diego State U; Jana Remy, Chapman U; Roopika Risam, Salem State U; Elizabeth Rodrigues, Grinnell College; Dylan Ruediger, American Historical Association; Rachel Schnepper, Wesleyan U; Anelise Hanson Shrout, Bates College; Margaret Simon, North Carolina State U; Mengchi Sun, U of Alberta; Lauren Tilton, U of Richmond; Michelle R. Warren, Dartmouth College.

The Escuela Nacional para Sordomudos (ENS), translated as the Mexican National School for the Deaf, opened its doors in the 1860s as part of the republic’s intention to educate its deaf people. The ENS did not use Lengua de Señas Mexicana (LSM), Mexico’s native sign language, for instruction, though they tolerated LSM use by the students. The school was closed permanently in 1972, thus leaving its former students still alive today as the last links to this historic institution. In this compelling social history, Claire L. Ramsey presents these unique Deaf Mexicans from their extraordinary experiences as ENS students and signers to their current personal lives.
One ENS signer, María de los Ángeles Bedolla, inspired the title of the book, The People Who Spell. In her account, she describes herself and her peers as cultured and educated compared to the young deaf people of today. The ENS signers pride themselves on el deletreo, LSM fingerspelling, which they consider key to their sophistication. Ramsey relates each of the signers’ childhoods, marriages, work experiences, and retirements. However, she brings threads of their stories together to reveal a common and abiding disappointment in modern-day Mexico’s failure to educate its deaf citizens according to the promise made more than 100 years ago. The narratives of the ENS signers detail their remarkable lives and heritage but also legitimately question the future of Mexico’s young deaf people.




From the birth of modern tennis in Victorian Britain to the present day, we bear witness to struggles around sexuality, gender, race and class that have transformed the nature of tennis and sport itself. A People's History of Tennis is populated by diverse voices, recounting the sport's gay origins, 'Workers' Wimbledon', battles for gender equality and more.
Going beyond center court, this book reveals the hidden history of the game, providing a rich account of the challenges faced and victories won.



Beneath the glitzy surface of the resorts and the seemingly cookie-cutter suburban sprawl of Las Vegas lies a vibrant and diverse ethnic life. People of varied origins make up the population of nearly two million and yet, until now, little mention of the city has been made in studies and discussion of ethnicity or immigration. The Peoples of Las Vegas: One City, Many Faces fills this void by presenting the work of seventeen scholars of history, political science, sociology, anthropology, law, urban studies, cultural studies, literature, social work, and ethnic studies to provide profiles of thirteen of the city’s many ethnic groups. The book’s introduction and opening chapters explore the historical and demographic context of these groups, as well as analyze the economic and social conditions that make Las Vegas so attractive to recent immigrants. Each group is the subject of the subsequent chapters, outlining migration motivations and processes, economic pursuits, cultural institutions and means of transmitting culture, involvement in the broader community, ties to homelands, and recent demographic trends.

Diverse in their languages and customs, the Native American peoples of the Great Lakes region—the Miamis, Ho-Chunks, Potawatomis, Ojibwas, and many others—shared a tumultuous history. In the colonial era their rich homeland became a target of imperial ambition and an invasion zone for European diseases, technologies, beliefs, and colonists. Yet in the face of these challenges, their nations’ strong bonds of trade, intermarriage, and association grew and extended throughout their watery domain, and strategic relationships and choices allowed them to survive in an era of war, epidemic, and invasion.
In Peoples of the Inland Sea, David Andrew Nichols offers a fresh and boundary-crossing history of the Lakes peoples over nearly three centuries of rapid change, from pre-Columbian times through the era of Andrew Jackson’s Removal program. As the people themselves persisted, so did their customs, religions, and control over their destinies, even in the Removal era. In Nichols’s hands, Native, French, American, and English sources combine to tell this important story in a way as imaginative as it is bold. Accessible and creative, Peoples of the Inland Sea is destined to become a classroom staple and a classic in Native American history.


Critics tend to focus on mass-produced materials and make claims about pornography as plasticized or commodified. In contrast, eminent historian Lisa Z. Sigel looks at what people made, rather than what they bought, revealing how people thought about sexuality for themselves. She also explores periods when these sexual artifacts were pilloried, ransacked, and destroyed, providing a unique document of rare nineteenth- and twentieth-century objects. Whalers and craftsmen, prisoners and activists, African Americans and feminists—all made their own pornography. Ranging across the full sweep of this output, The People’s Porn challenges preconceptions as it tells a new and fascinating story about American sexual history.

Since its establishment in 1949, the People's Republic of China has upheld a nationwide ban on pornography, imposing harsh punishments on those caught purchasing, producing, or distributing materials deemed a violation of public morality. A provocative contribution to Chinese media studies by a well-known international media researcher, People’s Pornography offers a wide-ranging overview of the political controversies surrounding the ban, as well as a fascinating glimpse into the many distinct media subcultures that have gained widespread popularity on the Chinese Internet as a result. Rounding out this exploration of the many new tendencies in digital citizenship, pornography, and activist media cultures in the greater China region are thought-provoking interviews with individuals involved.

In The People’s Zion, Joel Cabrita tells the transatlantic story of Southern Africa’s largest popular religious movement, Zionism. It began in Zion City, a utopian community established in 1900 just north of Chicago. The Zionist church, which promoted faith healing, drew tens of thousands of marginalized Americans from across racial and class divides. It also sent missionaries abroad, particularly to Southern Africa, where its uplifting spiritualism and pan-racialism resonated with urban working-class whites and blacks.
Circulated throughout Southern Africa by Zion City’s missionaries and literature, Zionism thrived among white and black workers drawn to Johannesburg by the discovery of gold. As in Chicago, these early devotees of faith healing hoped for a color-blind society in which they could acquire equal status and purpose amid demoralizing social and economic circumstances. Defying segregation and later apartheid, black and white Zionists formed a uniquely cosmopolitan community that played a key role in remaking the racial politics of modern Southern Africa.
Connecting cities, regions, and societies usually considered in isolation, Cabrita shows how Zionists on either side of the Atlantic used the democratic resources of evangelical Christianity to stake out a place of belonging within rapidly-changing societies. In doing so, they laid claim to nothing less than the Kingdom of God. Today, the number of American Zionists is small, but thousands of independent Zionist churches counting millions of members still dot the Southern African landscape.

The land of the United States is defined by vast distances encouraging human movement and migration on a grand scale. Consequently, American stories are filled with descriptions of human bodies walking through the land.
In Peregrinations, Amy T. Hamilton examines stories told by and about Indigenous American, Euroamerican, and Mexican walkers. Walking as a central experience that ties these texts together—never simply a metaphor or allegory—offers storytellers and authors an elastic figure through which to engage diverse cultural practices and beliefs including Puritan and Catholic teachings, Diné and Anishinaabe oral traditions, Chicanx histories, and European literary traditions.
Hamilton argues that walking bodies alert readers to the ways the physical world—more-than-human animals, trees, rocks, wind, sunlight, and human bodies—has a hand in creating experience and meaning. Through material ecocriticism, a reading practice attentive to historical and ongoing oppressions, exclusions, and displacements, she reveals complex layerings of narrative and materiality in stories of walking human bodies.
This powerful and pioneering methodology for understanding place and identity, clarifies the wide variety of American stories about human relationships with the land and the ethical implications of the embeddedness of humans in the more-than-human world.


We know a lot about how clothing and shoes are made cheaply, but very little about the process when they are made beautifully. In The Perfect Fit, Claudio E. Benzecry looks at the craft that goes into designing shoes for women in the US market, revealing that this creative process takes place on a global scale. Based on unprecedented behind-the-scenes access, The Perfect Fit offers an ethnographic window into the day-to-day life of designers, fit models, and technicians as they put together samples and prototypes, showing how expert work is a complement to and a necessary condition for factory exploitation.
Benzecry looks at the decisions and constraints behind how shoes are designed and developed, from initial inspiration to the mundane work of making sure a size seven stays constant. In doing so, he also fosters an original understanding of how globalization works from the ground up. Drawing on five years of research in New York, China, and Brazil, The Perfect Fit reveals how creative decisions are made, the kinds of expertise involved, and the almost impossible task of keeping the global supply chain humming.

Parenting today is virtually synonymous with worry. We want to ensure that our children are healthy, that they get a good education, and that they grow up to be able to cope with the challenges of modern life. In our anxiety, we are keenly aware of our inability to know what is best for our children. When should we toilet train? What is the best way to encourage a fussy child to eat? How should we protect our children from disease and injury?
Before the nineteenth century, maternal instinct—a mother’s “natural know-how”—was considered the only tool necessary for effective childrearing. Over the past two hundred years, however, science has entered the realm of motherhood in increasingly significant ways. In Perfect Motherhood, Rima D. Apple shows how the growing belief that mothers need to be savvy about the latest scientific directives has shifted the role of expert away from the mother and toward the professional establishment. Apple, however, argues that most women today are finding ways to negotiate among the abundance of scientific recommendations, their own knowledge, and the reality of their daily lives.

- Agnew's exclusive choices on which beers to try at each location
- Entries on every brewery's history and philosophy
- Information on tours, tasting rooms and attached pubs, and dining options and other amenities
- A survey of each brewery's brands, including its flagship beer plus seasonal brews and special releases
- Brewery equipment and capacity
- Nearby attractions
In addition, Agnew sets the stage with a history of Midwestern beer spanning the origins of the immigrant brewers who arrived in the 1800s to the homebrewers-made-good who have built a new kind of brewing culture founded on creativity, dedication to quality, and attention to customer feedback.
Informed and unique, A Perfect Pint's Beer Guide to the Heartland is the essential companion for beer aficionados and curious others determined to drink the best the Midwest has to offer.
Includes more than 150 full color images, including the region's most distinctive beer labels, trademarks, and company logos.

Accepted for generations as a legitimate and functional part of Byzantine civilization, eunuchs were prominent in both the imperial court and the church. They were distinctive in physical appearance, dress, and manner and were considered uniquely suited for important roles in Byzantine life. Transcending conventional notions of male and female, eunuchs lived outside of normal patterns of procreation and inheritance and were assigned a unique capacity for mediating across social and spiritual boundaries. This allowed them to perform tasks from which prominent men and women were constrained, making them, in essence, perfect servants.
Written with precision and meticulously researched, The Perfect Servant will immediately take its place as a major study on Byzantium and the history of gender.

Subject to the scrutiny of a remarkable array of gazes—inquisitors, theologians, religious reformers, confessors, poets, playwrights, and, not least among them, husbands—the bodies of perfect and imperfect wives elicited diverse readings. Dopico Black reveals how imperialism, the Inquisition, inflation, and economic decline each contributed to a correspondence between the meanings of these human bodies and “other” bodies, such as those of the Jew, the Moor, the Lutheran, the degenerate, and whoever else departed from a recognized norm. The body of the wife, in other words, became associated with categories separate from anatomy, reflecting the particular hermeneutics employed during the Inquisition regarding the surveillance of otherness.
Dopico Black’s compelling argument will engage students of Spanish and Spanish American history and literature, gender studies, women’s studies, social psychology and cultural studies.

In Perfectly Average, Anna Creadick investigates how and why "normality" reemerged as a potent homogenizing category in postwar America. Working with scientific studies, material culture, literary texts, film, fashion, and the mass media, she charts the pursuit of the"normal" through thematic chapters on the body, character, class, sexuality, and community.
Creadick examines such evidence as the "Norm and Norma" models produced during the war by sexologists and anthropologists—statistical composites of"normal" American bodies. In 1945, as thousands of Ohio women signed up for a Norma Look-Alike contest, a "Harvard Study of Normal Men" sought to define the typical American male according to specific criteria, from body shape to upbringing to blood pressure. By the early 1950s, the "man in the gray flannel suit" had come to symbolize what some regarded as the stultifying sameness of the "normalized" middle class. Meanwhile, novels such as From Here to Eternity and Peyton Place both supported and challenged normative ideas about gender, race, and sexuality, even as they worked to critique the postwar culture of surveillance—watching and being watched—through which normalizing power functioned.
As efforts to define normality became increasingly personal, the tensions em-bedded in its binary logic multiplied: Was normal descriptive of an average or prescriptive of an ideal? In the end, Creadick shows, a variety of statistics, assumptions, and aspirations converged to recast "normality" not as something innate or inborn, but rather as a quality to be actively pursued—a standard at once highly seductive and impossible to achieve because it required becoming perfectly average.


The idea that gender is a performance—a tenet of queer feminist theory since the nineties—has spread from college classrooms to popular culture. This transformative concept has sparked reappraisals of social expectations as well as debate over not just gender, but sex: what it is, what it means, and how we know it. Most scientific and biomedical research over the past seventy years has assumed and reinforced a binary concept of biological sex, though some scientists point out that male and female are just two outcomes in a world rich in sexual diversity.
In Performance All the Way Down, MacArthur Fellow and Pulitzer Prize finalist Richard O. Prum brings feminist thought into conversation with biology, arguing that the sexual binary is not essential to human genes, chromosomes, or embryos. Our genomes are not blueprints, algorithms, or recipes for the physical representation of our individual sexual essences or fates. In accessible language, Prum shows that when we look closely at the science, we see that gene expression is a material action in the world, a performance through which the individual regulates and achieves its own becoming. A fertilized zygote matures into an organism with tissues and organs, neurological control, immune defenses, psychological mechanisms, and gender and sexual behavior through a performative continuum. This complex hierarchy of self-enactment reflects the evolved agency of individual genes, molecules, cells, and tissues.
Rejecting the notion of an intractable divide between the humanities and the sciences, Prum proves that the contributions of queer and feminist theorists can help scientists understand the human body in new ways, yielding key insights into genetics, developmental biology, physiology. Sure to inspire discussion, Performance All the Way Down is a book about biology for feminists, a book about feminist theory for biologists, and a book for anyone curious about how our sexual bodies grow.


The performances that Román analyzes range from localized community-based arts events to full-scale Broadway productions and from the controversial works of established artists such as Tony Kushner to those of emerging artists. Román considers dances produced by the choreographers Bill T. Jones and Neil Greenberg in the mid-1990s as new aids treatments became available and the aids crisis was reconfigured; a production of the Asian American playwright Chay Yew’s A Beautiful Country in a high-school auditorium in Los Angeles’s Chinatown; and Latino performer John Leguizamo’s one-man Broadway show Freak. He examines the revival of theatrical legacies by female impersonators and the resurgence of cabaret in New York City. Román also looks at how the performing arts have responded to 9/11, the U.S. invasion of Afghanistan, and the second war in Iraq. Including more than eighty illustrations, Performance in America highlights the dynamic relationships among performance, history, and contemporary culture through which the past is revisited and the future reimagined.
READERS
Browse our collection.
PUBLISHERS
See BiblioVault's publisher services.
STUDENT SERVICES
Files for college accessibility offices.
UChicago Accessibility Resources
home | accessibility | search | about | contact us
BiblioVault ® 2001 - 2024
The University of Chicago Press









